Welcome to the cannabis science and research section. This section is here to discuss scientific ideas, applications and ideas regarding cannabis and growing cannabis. To become part of our online cannabis growing community click here to register.
Cannabinoids!
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Cannabinoids!
Cannabinoids
In this topic I'm going to cover the many cannabinoids found in cannabis. I'll try to go into detail about the effects and medical properties of the cannabinoids which have most effect. First I'll talk about cannabinoids in general.
What is a Cannabinoid
Cannabis contains many chemical compounds, these compounds have different effects. Terpenes give us flavours and smells that make the different strains we all love so different. I've done a topic on terpenes. The most important of the many compounds found in cannabis are cannabinoids.
Cannabinoids vary greatly in their effects, you have all heard of THC, this is the cannabinoid which gives us the high, We have all heard of CBD, this compound actually suppresses the effects of THC. There are many more cannabinoids in cannabis, some with remarkable qualities. I'm sure we are all aware of the medical benefits of cannabis, there will be many more discoveries I'm sure, these medical qualities came from the cannabinoids present in Cannabis.
Cannabis plants produce 113 cannabinoids, maybe more. Cannabinoids are produced within trichomes, these tiny little balls of goodness are what gives cannabis that crystal looking sugary effect. In recent years Cannabis plants, more importantly, strains have been bred to produce increased levels of the Cannabinoid THC.
THC is a psychoactive compound and is the main cannabinoid that gives us the high we experience from the glorious herb. I've mentioned that CBD suppresses this high, so breeders have over the years tried to produce strains with very little of this cannabinoid present. We now know that CBD has some amazing medical properties. Breeders are now trying to increase this compound in strains of cannabis for that reason.
There are many other cannabinoids with special benefits, In time and with research the benefits of these other cannabinoids will be recognized and used to treat many things. I'm going to go through some of the many cannabinoids further down this topic.
But first, did you know that your body makes its own version of cannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are our own version of cannabinoids, your body produces them. While they differ from cannabinoids found in cannabis, they do very similar things. They do this by reacting with cannabinoid receptors, these are present in all of brains. That's right....we have had these receptors all along.
How do cannabinoids work?
Cannabinoids work by attaching themselves to the cannabinoid receptors in your brain, when this happens they change how the surrounding cells function, this creates different effects depending on the cannabinoid present. There are cannabinoid receptors found around the body, not just the brain, once cannabinoids enter the blood they will make their way to these receptors. That's the interesting thing, we know how some of these cannabinoids react in the brain and around the body, some get you high, some have amazing medical properties, there is so much more to learn.
I will now go through some cannabinoids, their effects, medical benefits and so on.
In this topic I'm going to cover the many cannabinoids found in cannabis. I'll try to go into detail about the effects and medical properties of the cannabinoids which have most effect. First I'll talk about cannabinoids in general.
What is a Cannabinoid
Cannabis contains many chemical compounds, these compounds have different effects. Terpenes give us flavours and smells that make the different strains we all love so different. I've done a topic on terpenes. The most important of the many compounds found in cannabis are cannabinoids.
Cannabinoids vary greatly in their effects, you have all heard of THC, this is the cannabinoid which gives us the high, We have all heard of CBD, this compound actually suppresses the effects of THC. There are many more cannabinoids in cannabis, some with remarkable qualities. I'm sure we are all aware of the medical benefits of cannabis, there will be many more discoveries I'm sure, these medical qualities came from the cannabinoids present in Cannabis.
Cannabis plants produce 113 cannabinoids, maybe more. Cannabinoids are produced within trichomes, these tiny little balls of goodness are what gives cannabis that crystal looking sugary effect. In recent years Cannabis plants, more importantly, strains have been bred to produce increased levels of the Cannabinoid THC.
THC is a psychoactive compound and is the main cannabinoid that gives us the high we experience from the glorious herb. I've mentioned that CBD suppresses this high, so breeders have over the years tried to produce strains with very little of this cannabinoid present. We now know that CBD has some amazing medical properties. Breeders are now trying to increase this compound in strains of cannabis for that reason.
There are many other cannabinoids with special benefits, In time and with research the benefits of these other cannabinoids will be recognized and used to treat many things. I'm going to go through some of the many cannabinoids further down this topic.
But first, did you know that your body makes its own version of cannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are our own version of cannabinoids, your body produces them. While they differ from cannabinoids found in cannabis, they do very similar things. They do this by reacting with cannabinoid receptors, these are present in all of brains. That's right....we have had these receptors all along.
How do cannabinoids work?
Cannabinoids work by attaching themselves to the cannabinoid receptors in your brain, when this happens they change how the surrounding cells function, this creates different effects depending on the cannabinoid present. There are cannabinoid receptors found around the body, not just the brain, once cannabinoids enter the blood they will make their way to these receptors. That's the interesting thing, we know how some of these cannabinoids react in the brain and around the body, some get you high, some have amazing medical properties, there is so much more to learn.
I will now go through some cannabinoids, their effects, medical benefits and so on.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
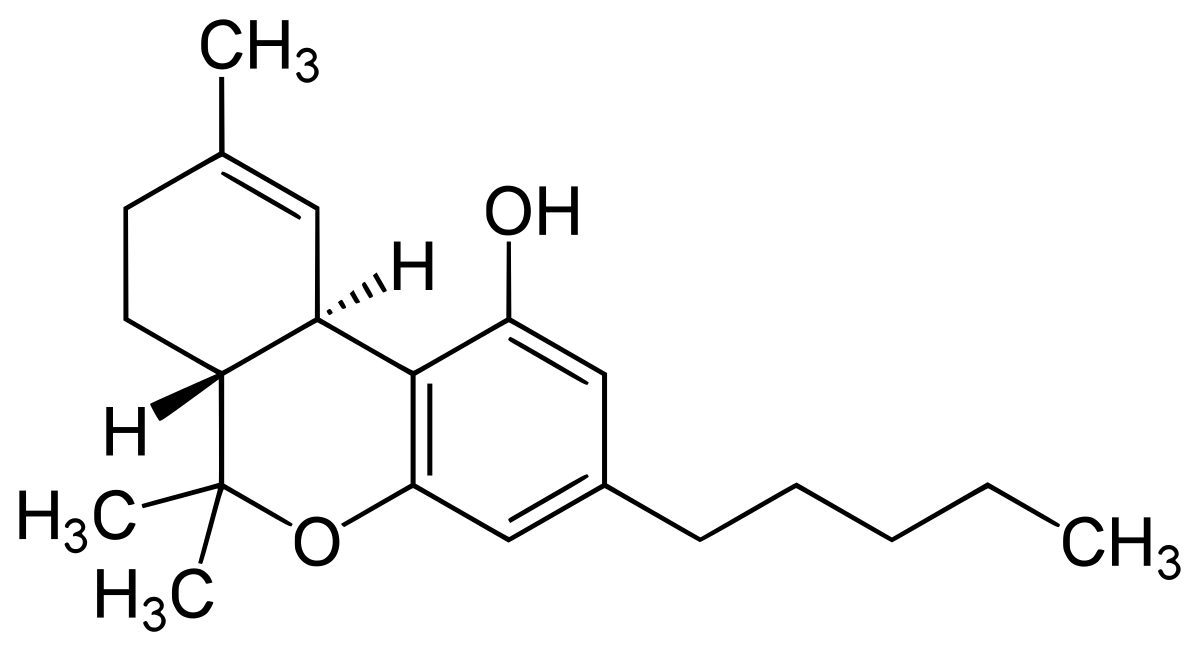
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
THC, the cannabinoid we will all be most familiar with. This is the most psychoactive cannabinoid. Its gives us that stoned feeling, strains have been bred to contain huge amounts of THC for this reason. In recent years the other benefits of this cannabinoid have been researched and acknowledged.
Therapeutic uses:
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Antioxidant – Prevents the damage of oxidation to other molecules in the body.
Antispasmodic – Suppresses muscle spasms.
Anxiolytic – While not fully recognized as an anxiolytic compound THC does seem to assist in the anxiety associated with PTSD.
Appetite Stimulant – THC is the only cannabinoid identified that is an appetite stimulant, giving people the stereotypical “munchies” many users describe.
Euphoriant – Produces feelings of euphoria, promotes happiness and relaxation.
Neuroprotective - Slows damage to the nervous system and brain.
Anorexia Nervosa - THC has shown great promise in reversing the weight loss associated with anorexia.
Cancer - THC was the first cannabinoid discovered that helped combat cancer, and since then it has been shown to halt the growth of tumours, and in some cases shrink them.
Chronic Pain - THC has been shown to have great prospect in treating chronic pain.
HIV/AIDS - Aside from assisting with the pain and nausea that often are associated with HIV/AIDS, THC directly fights the virus in unique ways.
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Recent research has shown THC to be a powerful treatment for Post Traumatic Stress Disorder.
Currently Being Studied For
Anorexia Nervosa: THC has shown great promise in reversing the weight loss associated with anorexia in studies on mice as well as humans. Even the synthetic cannabinoids Dronabinol and Marinol have been demonstrated to help with weight loss. While THC does stimulate one’s appetite, a double-blind placebo controlled study found that these effects were not strong enough to make THC a potential treatment for cachexia or anorexia.
Cancer: THC was the first cannabinoid discovered that helped combat cancer, and since then it has been shown to halt the growth of tumours, and in some cases shrink them, through various methods not yet fully understood. In one recent case study, an infant suffering from a brain tumour experienced a 90% reduction in tumour size over a year of twice a day use of hemp oil. Veteran cancer researcher Donald Tashkin, in the largest controlled study of its kind, found that daily smoking of THC-rich cannabis resulted in lower instances of cancer than in the general population of non-smokers! Think about it; all smoking causes cancer by creation of benzopyrene, but despite that THC is a strong enough anti-proliferative to prevent more cancer than the smoking causes.
Fun Fact: Burning ANY organic matter creates benzopyrene. This means that barbecue, toast, and even grilled vegetables can give you cancer, but cannabis will not even if you burn it.
Chronic Pain: THC has been shown to have great prospect in treating chronic pain because it seems to change “the way the nerves function.” THC also has been studied heavily for its use in treating neuropathic pain, including the pain associated with HIV and cancer. Recent studies seem to agree that THC changes how we feel pain and makes it more bearable. It is not a pain killer in the sense that it reduces the amount of pain felt, instead it seems to raise an individual’s pain tolerance by distracting them from their pain. A 2015 study on neuropathy in diabetic patients found that THC “demonstrated a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.”
Glaucoma: Robert Randall, the first medical cannabis patient in American history, and the man responsible for the passage of the federal medical cannabis program back in the 70’s, Compassionate Investigative New Drug Program, was using THC-rich cannabis to treat the intraocular pressure caused by his glaucoma until the day he died in 2001. A year after Randall died, a study in Pharmacology and Therapeutics was the first to find cannabinoid receptors in the eyes, giving some hints to THC’s effectiveness on glaucoma. Then in 2004, a study in the British Journal of Ophthalmology vindicated years of personal anecdotes and found that THC does reduce intraocular pressure, but the mechanism of action is still not fully understood. While most testing on cannabis use focus on smoking, a 2006 study on cannabis use and glaucoma looked at sublingual cannabis use. That study found that 5mg of THC administered sublingually reduced eye pressure without many side effects, the same study found that CBD either did nothing or worsened the eye pressure.
HIV/AIDS: Aside from assisting with the pain and nausea that often are associated with HIV/AIDS, THC directly fights the virus in unique ways that have only recently been identified. A 2012 study shows THC assisting in HIV treatment by its activation of CB2 receptors and CD4 receptors. Cannabis affects our body by interacting with our endocannabinoid system, the CB2 and CD4 receptors are a part of that system. A study from earlier this year expands on the role of THC in combating HIV through its activation of CB2 receptors.
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Recent research has shown THC to be a powerful treatment for Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, possibly due to it’s ability to help people forget. This forgetting can include forgetting about trauma that should be let go of, so the individual can heal and move forward. THC is a plant version of the endo-cannabinoid Anandamide, which has also been shown to be crucial in treating PTSD. Now, a host of scientists, including the award-winning researcher Sue Sisley, are conducting research into THC’s ability to help treat PTSD. Dr. Sisley has gained much attention after Dr. Sanjay Gupta covered her PTSD research in his CNN special, Weed III. Research by Dr. George Greer in New Mexico has shown that THC-rich cannabis can reduce symptoms of PTSD by 75% on average. A 2011 study from the University of Halfa demonstrated that marijuana, notably THC, can help mitigate the onset of PTSD if taken after a traumatic event.
Gastrointestinal Inflammation: THC lowers the incidence of blockages and other gastrointestinal inflammation associated with use of NSAID anti-inflammatory drugs. THC “protects against diclofenac-induced gastric inflammatory tissue damage at doses insufficient to cause common cannabinoid side effects.” A recent survey of Irritable Bowel Disorder sufferers found that 1/6 use THC-rich cannabis to treat the inflammation.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
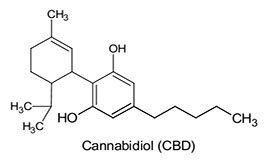
Cannabidiol (CBD)
CBD is a cannabiniod that in recent times has received a lot of attention in recent years dur to its many medical applications. I mentioned earlier in this topic that CBD couteracts the psycoactive effect of THC. This in itself is a benefit, some mdical applications that need the active THC cannabinoid present can have the effects of the high subdued or even removed. But thats not the only use for CBD, this cannabinoid has many mediacl applications itself.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows bacterial growth.
Anti-Diabetic – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that helps lower blood sugar levels.
Antidepressant – Relieves symptoms of depression.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-Epileptic – Reduces seizures and convulsions.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Insomnia – Aids with sleep.
Anti-Ischemic – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that reduces the risk of artery blockage.
Antipsioratic – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified to treat psoriasis.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Antipsychotic – Tranquilizing effects to relieve symptoms of psychosis, two terpenoids also help (linalool and myrcene).
Antioxidant – Prevents the damage of oxidation to other molecules in the body.
Antispasmodic – Suppresses muscle spasms.
Anxiolitic – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that relieves anxiety, but two terpenoids also help (linalool and limonene).
Bone Stimulant – Promotes bone growth.
Immunosuppressive – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that reduces function in the immune system.
Intestinal Anti-Prokinetic – CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that reduces small intestine contractions.
Neuroprotective – Slows damage to the nervous system and brain.
Vasorelaxant– CBD is the only cannabinoid identified that reduces vascular tension.
CBD is also currently being studied for a variety of conditions.
Currently Being Studied For
Alzheimer’s Disease/Dementia/Memory Loss: CBD’s strong neuroprotective and antioxidative effects work together to counteract the effects of aging on our brains, fighting off memory loss and dementia.
Bone Healing: New research from March 2015 has shown that CBD’s ability to stimulate bone growth is powerful enough to speed up and enhance the healing of broken bones. The same study found that THC had a related role in the healing of broken bones, working in entourage with CBD.
Cancer: A study was published in 2007, regarding ongoing research being done at San Francisco’s California Pacific Medical Center, showing that CBD inhibits a particular gene (Id-1) which is responsible for the growth of cancer cells in the body. By inhibiting this gene CBD shuts down the growth of cancer cells, potentially stopping or even reversing tumor growth. While it is premature to say that CBD cures cancer, it is worth further research.
Dravet Syndrome/Epilepsy: In October of 2013, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two clinical trials assessing the therapeutic uses of CBD in treating intractable epilepsy in children. The CBD preparations are being made by British pharmaceutical company GW Pharmaceuticals, makers of Sativex. Dravet is a rare seizure disorder where usually children will have their first intractable seizure before they are even one year old, and in exceptional cases seizures can last over 24 hours. Harborside, where I work, has a famous patient named Jayden, a young boy who uses a CBD-rich tincture to treat his Dravet Syndrome.
Depression/Anxiety: CBD stimulates the 5-HT1a receptor in the brain, a region involved in the re-uptake of serotonin and other processes that aid with depression and anxiety. The antidepressant properties of CBD are very similar to the trycyclic antidepressant Imipramine (also being evaluated for panic disorder).
Diabetes: CBD was first discovered to mitigate the effects of diabetes in 2006. since then it has been shown to have numerous benefits for people with diabetes, specifically in reducing neurotoxicity and inflammation. In a follow up study done in 2010, it was found that CBD worked as a defense against neurodegeneration. Another 2010 studysaid CBD had “great therapeutic potential in the treatment of diabetic complications, and perhaps other cardiovascular disorders.”
Inflammatory Bowel Disease/Crohn’s Disease: CBD shows a lot of promise for controlling the inflammatory responses and discomfort caused by Crohn’s disease and IBD. CBD has so much potential to regulate these diseases that it is being considered for a new class of IBD drugs.
Nausea: In a study done on nausea and vomiting, CBD was shown to have anti-emetic, anti-nausea effects. The same study found that CBG could block these anti-nausea effects, perhaps because moderate doses of CBD and CBG may oppose eachother at the 5HTP1a receptor in the brain.
Schizophrenia/Psychosis: CBD is a powerful antipsychotic currently being considered for use in treating schizophrenia and other psychoses. Cannabidiol appears to have a very similar chemical profile to certain atypical antipsychotic drugs.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
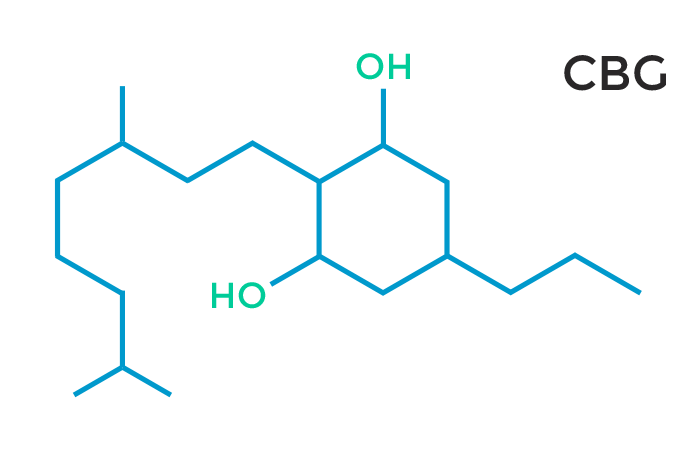
Cannabigerol (CBG)
Cannabigerol (CBG) is not considered psychoactive and is known to block the psychoactive effects of THC. It has been shown to stimulate the growth of new brain cells in a process called neurogenesis. Neurogenic compounds are extremely rare, which makes CBG a very worthwhile subject for more research. CBG also is antibacterial, anti-tumor, and aids with insomnia. CBG is considered a ‘stem cell’ cannabinoid and can change into different cannabinoids, altering the overall effects of the plant. CBG ,CBD, and the CBC’s all share the same molecular formula and weight, but have a different configuration.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows bacterial growth.
Anti-Epileptic – Reduces seizures and convulsions.
Anti-Inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Insomnia – Aids with sleep.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Bone Stimulant – Promotes bone growth.
Neurogenic – CBG is the only cannabinoid identified that helps stimulate the growth of new brain cells.
Currently Being Studied For
Glaucoma: A 2009 study found both CBG and THC to be very effective for relieving the intraocular pressure from glaucoma. This is an area that will undoubtedly be receiving more research in the years to come.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Much like CBD, CBG shows a lot of potential for controlling the inflammation that leads to IBD, and like CBD warrants further research.
Painkiller and Anti- Inflammatory: Recent research suggests that CBG has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties and recommends further study.
5-HT1a Receptor Agonist/Antagonist?: CBG appears to do something at the 5-HT1a receptor that is not fully understood. It modulates the effects of other cannabinoids at this brain site, which is the hub of emotions and depression regulation in the brain. Depending on the study, evidence suggests that CBG may help with depression and anxiety, or possibly block certain anti-depressant drugs. One study in rodents showed that if the right combination of CBG and CBD were present the CBG would block some of the anti-nausea effects of the CBD, but it could not quite identify why (other than it related to the 5HT1a receptor).
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
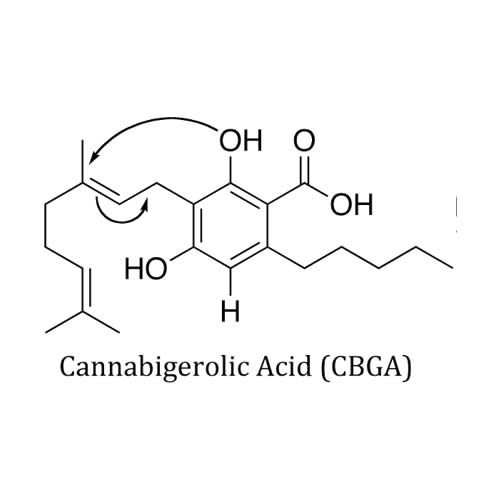
Cannabinoid Profile: Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGa)
Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa) is formed when geranyl pyrophosphate combines with olivetolic acid within the cannabis plant. It is thanks to CBGa that all other medicinal effects of cannabis are possible. Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa) can be thought of as the stem cell cannabinoid, which becomes THCa/THC, CBDa/CBD, CBCa/CBC, and CBG. It does this through different types of biosynthesis, where chemicals combine to form new compounds, examples being the THC biosynthase and the CBD biosynthase. Hemp strains of cannabis have higher amounts of CBG due to a recessive trait, which may imply higher amounts of CBGa present in those strains as well.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows bacterial growth.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth through apoptosis.
Currently Being Studied For
Cannabinoid Biosynthase: Nearly all current research on CBGa focuses solely on its role in the biosynthesis of other cannabinoids. Virtually no money is going to study its analgesic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative properties.
We learned in 2005 that the enzyme controlling the conversion of CBGa into THCa and further THC is held within the trichomes of the plant. This makes sense, as the trichomes have long been known to be the home of THC. Sirikantaramas did a follow up study on his 2005 research which showed they could grow THCa in a laboratory using a yeast culture as a host. If you want to know more about the THCa synthase, which is the first biosynthase to see any major study, you can look at this 2009 literature review profiling it. It wasn’t until 2014 that any of this research turned back to focus on CBGa again, when Alaoui et Al (2014) identified how and where CBGa binding happened, then explored how it was converted into THCa. Their research could be key to better understanding how THCa works.
Cancer: While there are no current studies being done on CBGa for its abilities to help with cancer, it has been shown to be an anti-proliferative just like CBG, THC, and CBD. CBGa encourages apoptosis, which is also known as programmed cell death. Defective apoptosis is believed to be a major reason for the formation and progression of cancer, so oncologists are naturally eager to find new ways to stimulate that bodily response. Cannabinoids appear to stimulate apoptosis in previously unknown ways, posing a novel way to mitigate and potentially cure cancer. While this much is known about CBGa, more research should be done.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
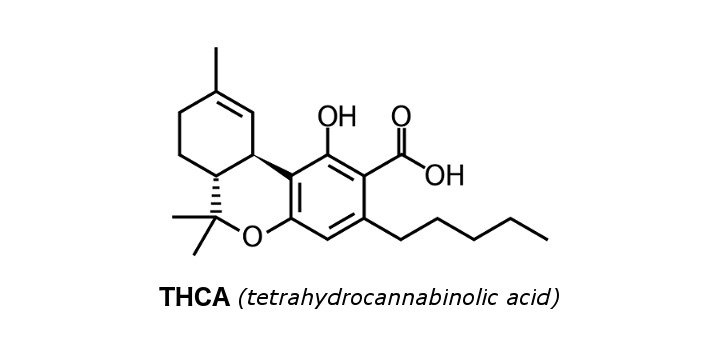
Cannabinoid Profile: Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THCa)
Found in the trichomes, Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa) is the acidic precursor to THC, which actually exists in only minute quantities in the living plant. In living cannabis, THCa is the most abundant cannabinoid and terpenoid, potentially reaching over 30% of the dry weight of any cannabis plant. Immediately after harvest, the THCa begins to be converted into THC, a process quickened by exposure to heat and sunlight. One main reason cannabis is cured is to convert the THCa into THC, as well as drying it out to make it easier to burn, thus releasing the remaining THCa as THC. Knowing about decarboxylating cannabis is crucial in making edibles, where one pre-cooks the bud before making it into butter to raise the potency by converting THCa into THC.
Like all cannabinoids that exist in the living cannabis plant, THCa is non-psychoactive, though it still stimulates the appetite like THC. It also is a powerful anti-inflammatory, helps fight cancer and other tumors, aids with sleep, and more. Also like THC, an oral test has already been developed to detect THCa. While some sources show THCa to be a stable compound, Aphios research chemicals claims that it is very unstable and will breakdown into THC within weeks. It may have to do with the preparation of synthesized THCa used in their laboratory versus an active live-plant based THCa, but without further research the stability of THCa and how quickly it converts to THC is unknown.
Therapeutic Uses
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-Inflammatory – Reduces inflammation.
Anti-Insomnia – Aids with sleep.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Antispasmodic – Suppresses muscle spasms.
Modulates Immune System – THCa has been shown to both improve and potentially suppress the immune system functions.
Neuroprotective – Slows damage to the nervous system and brain.
Currently Being Studied For
Anti-Emetic: THC has long been recognized as a valuable tool in combating nausea, but research done in 2013 found that THCa may be even more effective at preventing nausea and vomiting than THC. This means that patients suffering from nausea who do not want the psychoactive effects of THC should consider THCa.
Cancer: Many sources online claim that THCa helps fight cancer, but few studies have been done examining the cancer-fighting properties of this non-psychoactive cannabinoid. This 2011 study hints at the anti-tumor properties of THCa but its main focus was on the interaction of various cannabinoids and the TRP protein receptor channel. A 2013 study looking at prostate cancer also found THCa to be effective but did not elaborate on the mechanisms used or recommend further study.
Lupus: While no formalized studies are being done on THCa and Lupus, Dr. William Courtney and his wife Kristen have anecdotally demonstrated that fresh juiced cannabis high in THCa can control Lupus. As Kristen is still alive and managing her Lupus this study is ongoing, and still a success.
Neuroprotective: A 2012 study done on cell cultures shows that THCa may be a mild neuroprotective compounds for certain classes of brain cells, preventing unwanted cell death. These effects do not seem as notable as the neuroprotective qualities of THC and CBD but they are certainly worth more research.
The THCa/CBGa Process: Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa), CBG, THCa, THC, CBD, and CBC are all related compounds formed from the same chemical processes. CBGa and THCa, are the originator compounds that morph into the others. This linkage was explored in this 2012 study but needs further research to fully understand the mechanisms it works through.
*Note: Decarboyxlation – A chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases CO2, often triggered by heat or exposure to sunlight.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
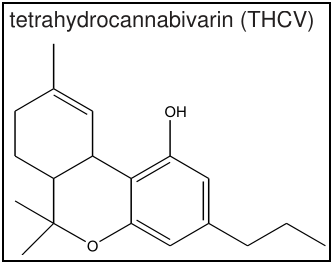
Cannabinoid Profile: Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCv)
THCv is a non-psychoactive variant of THC. The other major difference between the two is that instead of stimulating appetite, the famed ‘munchies,’ THCv actually suppresses appetite. For that reason THCv is being heavily researched as a weight loss tool. Like many cannabinoids it is an anti-inflammatory and an analgesic, though less strong than CBD and THC, but using different mechanisms in the body.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Anorectic – Appetite suppressant, promotes weight loss.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-Epileptic – Reduces seizures and convulsions.
Anti-Inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Bone Stimulant – Promotes bone growth.
Euphoriant – Produces feelings of euphoria, promotes happiness and relaxation.
Currently Being Studied For
Diabetes: A combination CDB/THCv tincture is in a phase 2 clinical trial as a way to mitigate diabetes. GW Pharmaceuticals, a British company, is a world leader in cannabis research. GW is presently examining CBD/THCv’s abilities to ameliorate insulin sensitivity.
Weight Loss: The same mechanisms that allow THCv to combat diabetes combined with THCv’s anorectic properties make it an effective way to combat obesity and control weight gain. GW Pharmaceuticals is also leading this research. GW believes in THCv so much they have even patented its abilities to combat weight gaining and diabetes.
Parkinson’s Disease: THCv is a cannabinoid that has been identified that can aid in Parkinson’s Disease by attenuating the motor inhibition caused by 6-hydroxydopamine. It also has various related mechanisms that assist in treating Parkinson’s.
Anti-Inflammatory: This study was only done on mice but if other studies are any indication of success it should apply similarly to humans, but THCv shows to be an anti-inflammatory. It works through a different mechanism than other anti-inflammatory drugs, THCv inhibits cyclic AMP production by hCB(2) CHO cells, but does not inhibit other affiliated cells. The whole thing seemed to rely on the CB 2 receptors.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
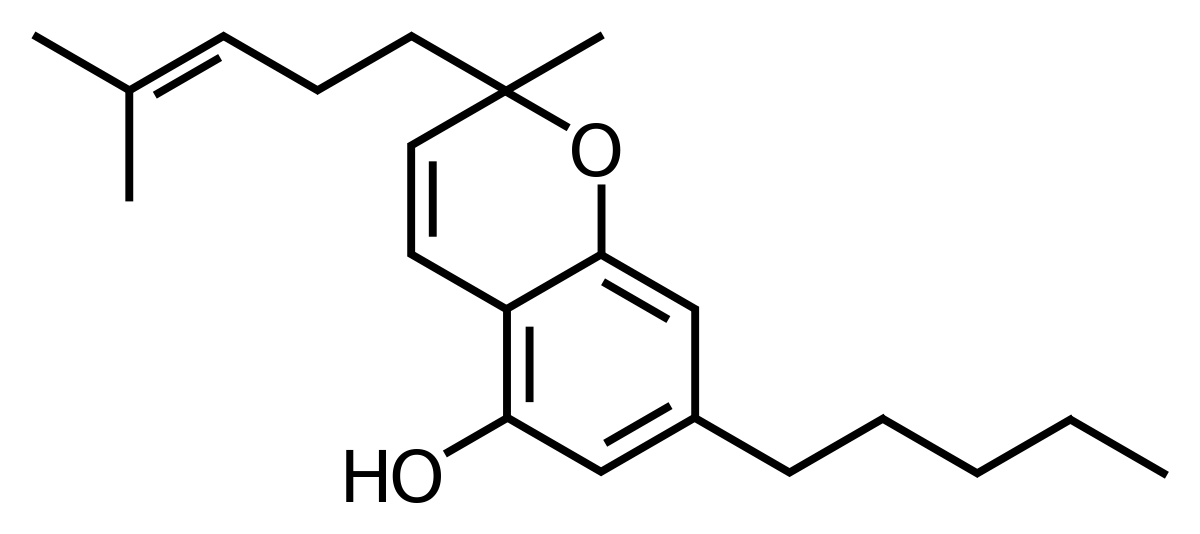
Cannabinoid Profile: Cannabichromene (CBC)
Cannabichromene is a little understood non-psychoactive cannabinoid that has recently been the subject of much greater scrutiny. Like THC and CBD, CBC is an end product of CBG being processed into CBGa, and then into other cannabinoids. As a result, CBC has the same chemical formula and weight as CBD and THC but differs from its chemical cousins by the arrangement of its atoms. The heretofore lack of research hasn’t stopped it from being the subject of multiple patents recognizing its wide range of medical uses. Like THC and CBD, CBC is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory, although less potent than these more famous molecules. It is also antibacterial and its variant CBCa has been shown to be an antifungal agent. Like CBD, cannabichomene is both a bone stimulant and neurogenic compound, helping grow both body and mind. Perhaps its most important use is as an anti-proliferative, slowing tumor growth and combating cancer, just like CBD and THC. CBC has also been shown to be ten times as powerful as CBD at reducing anxiety and stress. Finally, like other cannabinoids, CBC will convert into another cannabinoid through decarboxylation by UV light, though instead of becoming CBN, it becomes CBL, a cannabinoid we known relatively nothing about.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Antidepressant – Relieves symptoms of depression.
Antifungal – Inhibits the growth of fungus.
Anxiolitic – Relieves anxiety.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Bone Stimulant – Promotes bone growth.
Neurogenesis – Promotes the growth of new brain cells.
Currently Being Studied For
Analgesic: While only a study on rats, CBC was been shown to have great promise as an analgesic painkiller, perhaps as good as CBD.
Antidepressant: In this 2010 study, both THC and CBC were shown to display significant antidepressant qualities and “contribute to the overall mood-elevating properties of cannabis.”
Anti-Inflammatory: In two other recent studies on rats CBC was shown to be a powerful anti-inflammatory. Interestingly it was found that the mechanism of action did not involve CB1, CB2, or the TRPA1 receptors, like with THC and CBD; this is certainly worth more research as it could imply another type of receptor site is present.
Neurogenesis: A study done last year confirms that CBC stimulates bone growth. As neurogenic compounds are very rare this makes CBC a very important cannabinoid worth significant research. This could make CBC useful in treating the Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative conditions, but that will need more research.
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
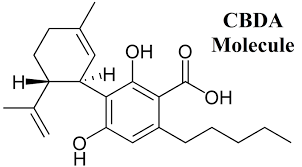
Cannabinoid Profile: Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDa)
Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDa) is one of the four possible outcomes of Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa) being processed into cannabigerol (CBG), Cannabichromic acid (CBCa), Tetrahydrocannabibolic acid (THCa), and CBDa. CBGa is processed into other cannabinoids by synthase enzymes, and the CBDa synthase was first purified and isolated in 1996. Coincidentally, this was the same year California passed Prop 215 and became the first medical cannabis state.
Until recently, CBDa was thought to be a minor cannabinoid and only be a small part of the overall cannabinoid profile. Higher amounts have been seen in ruderalis strains and recent hybrids like Cannatonic C-6 and ACDC have elevated levels of CBDa at potentially higher levels than THCa. Just like THCa, when heated up CBDa decarboxylates; as THCa becomes THC, so CBDa becomes CBD. Like CBD, CBDa is not psychoactive. While there hasn’t been much research done on CBDa yet, the research that has been done is quite promising. It appears to have anti-emetic effects as well as anti-proliferative effects, making it ideal for fighting cancer.It also has been shown to be an anti-inflammatory and to possess anti-bacterial properties.
Therapeutic Uses
Antibacterial – Slows bacterial growth.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth
Currently Being Studied For
Anti-Bacterial: Leizer et al (2000) mention a strong correlation between the levels of CBDa in a plant and the CBD levels of the plant after synthase. They also mention that more CBDa present will mean greater antimicrobial potency in the resulting CBD. They do not explain the mechanisms at work.
Anti-Emetic: A 2013 study shows that CBDa reduces vomiting and nausea by increasing activity at the 5-HT1A receptor. This means that CBDa can be used as a non-psychoactive alternative to THC to prevent vomiting and nausea. This isn’t the first study to show this, as a 2011 study found that CBDa functioned as an anti-emetic but did not pin the relation to the 5-HT1A receptor. More research should be done to properly explore this exciting new medicinal use for CBDa.
Anticipatory Nausea: Anticipatory Nausea (AN) is a condition where someone vomits due to neutral stimuli, before they are actually nauseous. AN is very common in patients receiving chemotherapy, with roughly 29% developing it. AN appears to be the result of classical conditioning; given enough exposures to neutral stimuli, like the smells of the chemotherapy room, a susceptible person will begin to vomit before even receiving treatment. In a 2014 study, CBDa was shown to be a very effective treatment for sufferers of AN. In 2013, the same group of researchers found that CBDa was an effective treatment for acute nausea in chemotherapy patients.
Cancer: In 2012 CBDa joined THC, CBD, and numerous other cannabinoids that are anti-proliferatives. These cannabinoids control the growth of cancerous tumors. Takeda et al (2012) found that CBDa could inhibit the migration of human breast cancer cells. This government funded study recognized CBDa’s potential to mitigate the effects of cancer even in its more aggressive forms.”The data presented in this report suggest for the first time that [a] component in the cannabis plant, CBDA, offers potential therapeutic modality in the abrogation of cancer cell migration, including aggressive breast cancers.”
- Keeno
- Registered User
- Posts: 25547
- Joined: Sat Oct 07, 2017 10:11 pm
- Has thanked: 11290 times
- Been thanked: 17540 times
- Contact:
- Status: Offline
Re: Cannabinoids!
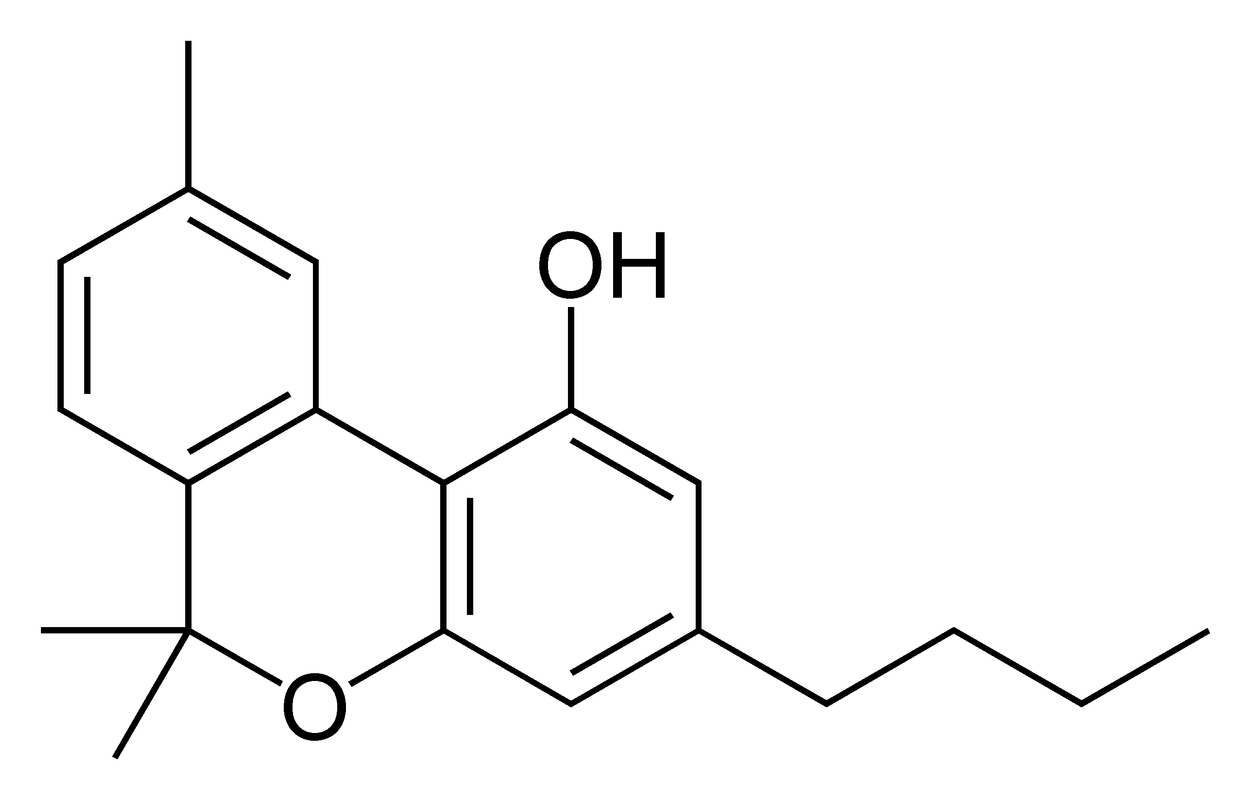
Cannabinoid Profile: Cannabinol (CBN)
Cannabinol (CBN) is what tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) will break down into over time due to exposure to oxygen and heat. By this time CBN will become only mildly psychoactive, and much less intense than when it was THC. However, just because this cannabinoid isn’t very psychoactive doesn’t mean it isn’t potent. In fact, CBN is the strongest cannabinoid identified for promoting sleep, which makes cannabis rich in CBN an ideal treatment for insomnia. Indica strains appear to have more CBN than sativa strains, which would explain the commonly held belief that indicas make you sleepy and give you a body high. CBN is a CB2 and CB1 receptor agonist and may inhibit immune cell functionality.
Therapeutic Uses
Analgesic – Relieves pain.
Antibacterial – Slows bacterial growth.
Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting and nausea.
Anti-Epileptic – Reduces seizures and convulsions.
Anti-inflammatory – Reduces inflammation systemically.
Anti-Insomnia – Aids with sleep.
Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth.
Appetite Stimulant – CBN appears to be a mild appetite stimulant.
Bone Stimulant – Promotes bone growth by stimulating osteocytes.
Currently Being Studied For
Analgesic: Both THC and CBN have been identified as pain killers, though THC is far more powerful. A 2002 study identified that both THC and CBN cause a release of certain gene-related peptides from sensory nerves and are the only identified cannabinoids to use this mechanism.
Appetite Stimulant: Everyone knows that THC stimulates the appetite, giving users the ‘munchies’ that many people describe. It was only in 2012 that it was discovered that CBN also stimulates the appetite, though this effect appears to be not as strong as THC.
Cancer: A 2006 study revealed that CBN joins THC and numerous other cannabinoids in having the ability to control the growth of cancer cells. CBN specifically was found to control a type of lung tumor known as a Lewis carcinoma.